# Vue源码解读(一)
# 一、Vue初始化流程
Vue源码学习流程如下,以下文件都在src目录下。
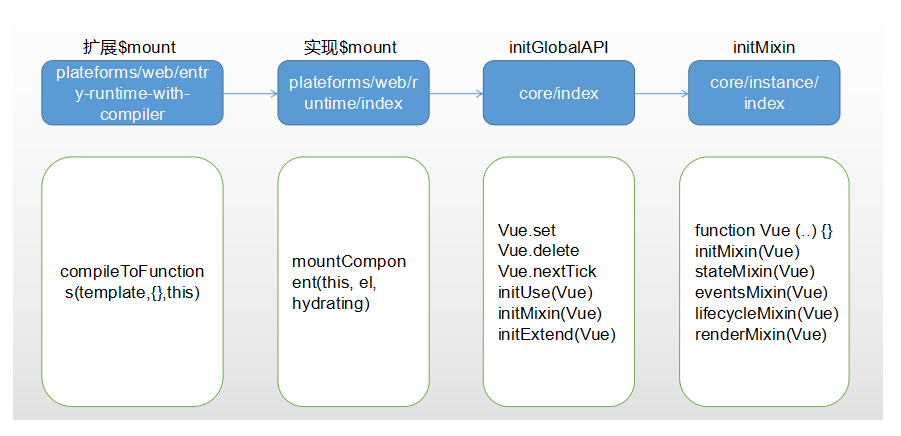
# 入口
src\platforms\web\entry-runtime-with-compiler.js,扩展$mount。
// 扩展默认$mount方法:能够编译template或el指定的模板
const mount = Vue.prototype.$mount
Vue.prototype.$mount = function(
el ? : string | Element,
hydrating ? : boolean
): Component {
// 获取选项
const options = this.$options
// 不存在render选项,则将template/el的设置转换为render函数
if (!options.render) {
let template = options.template
if (template) {
// 解析template选项
} else if (el) {
// 否则解析el选项
template = getOuterHTML(el)
}
if (template) {
// 编译得到render函数
const {
render,
staticRenderFns
} = compileToFunctions(template, {..
}, this)
options.render = render
}
}
// 执行默认$mount函数
return mount.call(this, el, hydrating)
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
src\platforms\web\runtime\index.js,实现$mount,核心就一个mountComponent;定义一个__patch__方法。
Vue.prototype.__patch__ = inBrowser ? patch : noop
Vue.prototype.$mount = function(
el ? : string | Element,
hydrating ? : boolean
): Component {
el = el && inBrowser ? query(el) : undefined
// 挂载组件
return mountComponent(this, el, hydrating)
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
src\core\index.js,初始化全局api
import Vue from './instance/index'
import { initGlobalAPI } from './global-api/index'
initGlobalAPI(Vue)
/// 省略其它代码
2
3
4
5
src\core\instance\index.js,实现Vue构造函数,实现若干实例方法和属性。 Vue的核心就在src\core\instance\目录里面。
import { initMixin } from './init'
import { stateMixin } from './state'
import { renderMixin } from './render'
import { eventsMixin } from './events'
import { lifecycleMixin } from './lifecycle'
function Vue (options) {
this._init(options); // _init方法在initMixin里面定义
}
initMixin(Vue)
stateMixin(Vue)
eventsMixin(Vue)
lifecycleMixin(Vue)
renderMixin(Vue)
export default Vue
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
# Vue全局API
src\core\global-api\index.js,定义全局api
// 省略了部分代码
import { initUse } from './use'
import { initMixin } from './mixin'
import { initExtend } from './extend'
import { initAssetRegisters } from './assets'
import { set, del } from '../observer/index'
import {nextTick} from '../util/index'
export function initGlobalAPI (Vue: GlobalAPI) {
Vue.set = set
Vue.delete = del
Vue.nextTick = nextTick
initUse(Vue)
initMixin(Vue)
initExtend(Vue)
initAssetRegisters(Vue)
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
# initMixin(Vue)
src\core\instance\init.js,实现vue初始化函数_init,会初始化生命周期、事件、渲染器、注入、状态等等。
Vue.prototype._init = function (options?: Object) {
// 省略其它代码
initLifecycle(vm) // 初始化生命周期
initEvents(vm) // 初始化事件
initRender(vm) // 初始化渲染器
callHook(vm, 'beforeCreate') // 调用beforeCreate钩子
initInjections(vm) // resolve injections before data/props
initState(vm) // 初始化状态
initProvide(vm) // resolve provide after data/props
callHook(vm, 'created')
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
由此可以得知,在beforeCreate之前会初始化生命周期、初始化事件、初始化渲染器。在beforeCreate之后,created之前会初始化注入、初始化状态。
- initLifecycle
src\core\instance\lifecycle.js,把组件实例里面用到的常用属性初始化。
vm.$parent = parent
vm.$root = parent ? parent.$root : vm
vm.$children = []
vm.$refs = {}
2
3
4
5
- initEvents
src\core\instance\events.js,父组件传递的需要处理的事件。
vm._events = Object.create(null)
vm._hasHookEvent = false
// init parent attached events
const listeners = vm.$options._parentListeners
if (listeners) {
updateComponentListeners(vm, listeners)
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
- initRender
src\core\instance\render.js,$slots的初始化,$createElement函数的申明,$attrs和$listeners的响应化。
vm.$slots = resolveSlots(options._renderChildren, renderContext)
vm.$scopedSlots = emptyObject
vm._c = (a, b, c, d) => createElement(vm, a, b, c, d, false)
vm.$createElement = (a, b, c, d) => createElement(vm, a, b, c, d, true)
defineReactive(vm, '$attrs', parentData && parentData.attrs || emptyObject, null, true)
defineReactive(vm, '$listeners', options._parentListeners || emptyObject, null, true)
2
3
4
5
6
7
- initState
src\core\instance\state.js,初始化状态,比如props、methods、data、computed、watch。
vm._watchers = []
const opts = vm.$options
if (opts.props) initProps(vm, opts.props)
if (opts.methods) initMethods(vm, opts.methods)
if (opts.data) {
initData(vm); // 数据响应化
} else {
observe(vm._data = {}, true /* asRootData */)
}
if (opts.computed) initComputed(vm, opts.computed)
if (opts.watch && opts.watch !== nativeWatch) {
initWatch(vm, opts.watch)
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
# stateMixin(Vue)
src\core\instance\state.js,定义$data,$props两个实例属性和$set,$delete,$watch三个实例方法。
export function stateMixin (Vue: Class<Component>) {
const dataDef = {}
dataDef.get = function () { return this._data }
const propsDef = {}
propsDef.get = function () { return this._props }
Object.defineProperty(Vue.prototype, '$data', dataDef)
Object.defineProperty(Vue.prototype, '$props', propsDef)
Vue.prototype.$set = set
Vue.prototype.$delete = del
Vue.prototype.$watch = function (
expOrFn: string | Function,
cb: any,
options?: Object
): Function {
const vm: Component = this
if (isPlainObject(cb)) {
return createWatcher(vm, expOrFn, cb, options)
}
options = options || {}
options.user = true
const watcher = new Watcher(vm, expOrFn, cb, options)
if (options.immediate) {
try {
cb.call(vm, watcher.value)
} catch (error) {
handleError(error, vm, `callback for immediate watcher "${watcher.expression}"`)
}
}
return function unwatchFn () {
watcher.teardown()
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
# eventsMixin(Vue)
src\core\instance\events.js,定义事件相关实例,$on,$off,$once,$emit。
export function eventsMixin (Vue: Class<Component>) {
const hookRE = /^hook:/
Vue.prototype.$on = function (event: string | Array<string>, fn: Function): Component {}
Vue.prototype.$once = function (event: string, fn: Function): Component {}
Vue.prototype.$off = function (event?: string | Array<string>, fn?: Function): Component {}
Vue.prototype.$emit = function (event: string): Component {}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
# lifecycleMixin(Vue)
src\core\instance\lifecycle.js,实现组件生命周期相关的三个核心实例api,_update、$forceUpdate、$destroy。
export function lifecycleMixin (Vue: Class<Component>) {
Vue.prototype._update = function (vnode: VNode, hydrating?: boolean) {
if (!prevVnode) {
vm.$el = vm.__patch__(vm.$el, vnode, hydrating, false /* removeOnly */)
} else {
vm.$el = vm.__patch__(prevVnode, vnode)
}
}
Vue.prototype.$forceUpdate = function () {}
Vue.prototype.$destroy = function () {}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
# renderMixin(Vue)
src\core\instance\render.js,定义$nextTick和_render。
export function renderMixin (Vue: Class<Component>) {
Vue.prototype.$nextTick = function (fn: Function) {
return nextTick(fn, this)
}
Vue.prototype._render = function (): VNode {
const vm: Component = this
const { render, _parentVnode } = vm.$options
vm.$vnode = _parentVnode
let vnode
try {
vnode = render.call(vm._renderProxy, vm.$createElement)
} catch (e) {
vnode = vm._vnode
}
} finally {
currentRenderingInstance = null
}
// set parent
vnode.parent = _parentVnode
return vnode
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
# 二、Vue数据响应式
vue数据响应化的代码都在src\core\observer\目录里面,具体实现是在Vue初始化时,会调用initState,它会初始化data,props等,这里着重关注data初始化,src\core\instance\state.js,initData核心代码是将data数据响应化,实现数据响应式的原理是数据劫持+发布/订阅模式。
# observe
observe方法返回一个Observer实例,src\core\observer\index.js,核心代码如下
export function observe (value: any, asRootData: ?boolean): Observer | void {
if (!isObject(value) || value instanceof VNode) {
return
}
let ob: Observer | void
// 判断该对象是否有__ob__实例属性
if (hasOwn(value, '__ob__') && value.__ob__ instanceof Observer) {
ob = value.__ob__
} else if (
shouldObserve &&
!isServerRendering() &&
(Array.isArray(value) || isPlainObject(value)) &&
Object.isExtensible(value) &&
!value._isVue
) {
ob = new Observer(value) // 创建Observer实例
}
if (asRootData && ob) {
ob.vmCount++
}
return ob
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
# Observer
Observer对象根据数据类型执行对应的响应化操作,src\core\observer\index.js,核心代码如下
export class Observer {
value: any;
dep: Dep;
vmCount: number; // number of vms that have this object as root $data
constructor (value: any) {
this.value = value
this.dep = new Dep()
this.vmCount = 0
def(value, '__ob__', this) // 定义__ob__实例属性,后面就可以直接引用这个Observer实例
if (Array.isArray(value)) {
if (hasProto) {
protoAugment(value, arrayMethods)
} else {
copyAugment(value, arrayMethods, arrayKeys)
}
this.observeArray(value) // 数组响应化
} else {
this.walk(value) // 对象响应化
}
}
// 对象响应化
walk (obj: Object) {
const keys = Object.keys(obj)
for (let i = 0; i < keys.length; i++) {
defineReactive(obj, keys[i]) // 定义对象属性的getter/setter,getter负责添加依赖,
//setter负责通知更新
}
}
// 数组响应化
observeArray (items: Array<any>) {
for (let i = 0, l = items.length; i < l; i++) {
observe(items[i]) // 对数组的每一个元素调用observe方法
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
# defineReactive
defineReactive定义对象属性的getter/setter,getter负责添加依赖,setter负责通知更新。核心代码如下
export function defineReactive (
obj: Object,
key: string,
val: any,
customSetter?: ?Function,
shallow?: boolean
) {
const dep = new Dep() // 创建dep实例,一个key一个Dep实例,用来管理该key的所有watcher
let childOb = !shallow && observe(val) // 递归执行子对象响应化
Object.defineProperty(obj, key, { // 定义当前对象getter/setter
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
get: function reactiveGetter () {
const value = getter ? getter.call(obj) : val
if (Dep.target) {
dep.depend() // getter被调用时若存在依赖则追加
if (childOb) {
childOb.dep.depend() // 若存在子observer,则依赖也追加到子ob
if (Array.isArray(value)) {
dependArray(value) // 数组需特殊处理
}
}
}
return value
},
set: function reactiveSetter (newVal) {
const value = getter ? getter.call(obj) : val
if (newVal === value || (newVal !== newVal && value !== value)) {
return
}
val = newVal
childOb = !shallow && observe(newVal)
dep.notify() // 调用notify方法通知watcher去执行对应的更新函数
}
})
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
# Dep
负责管理一组Watcher,包括watcher实例的增删及通知更新,src\core\observer\dep.js,核心代码如下
export default class Dep {
static target: ?Watcher; // 保存当前watcher实例(watcher实例里面会包含当前Dep的信息),
//全局唯一
id: number;
subs: Array<Watcher>;
constructor () {
this.id = uid++
this.subs = [] // 保存若干watcher
}
addSub (sub: Watcher) {
this.subs.push(sub) // 添加watcher
}
removeSub (sub: Watcher) {
remove(this.subs, sub) // 移除watcher
}
//watcher和dep相互保存引用
depend () {
// 如果Dep.target有值,则说明已经创建了watcher并触发了getter,
// 使得Dep.target保存了watcher实例
if (Dep.target) {
Dep.target.addDep(this);// 往Dep.target添加自己,addDep方法在watcher类里面定义。
}
}
notify () {
const subs = this.subs.slice()
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && !config.async) {
subs.sort((a, b) => a.id - b.id)
}
for (let i = 0, l = subs.length; i < l; i++) {
subs[i].update()
}
}
}
// 创建全局唯一的watcher
Dep.target = null
const targetStack = []
export function pushTarget (target: ?Watcher) {
targetStack.push(target) // 添加watcher
Dep.target = target
}
export function popTarget () {
targetStack.pop() // 移除watcher
Dep.target = targetStack[targetStack.length - 1]
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
# Watcher
Watcher解析一个表达式并收集依赖,当数值变化时触发回调函数,常用于$watch API和指令中。
每个组件也会有对应的Watcher,数值变化会触发其update函数导致重新渲染。
src\core\observer\watcher.js,核心代码如下
export default class Watcher {
constructor (
vm: Component,
expOrFn: string | Function,
cb: Function,
options?: ?Object,
isRenderWatcher?: boolean
) {
this.vm = vm
// ...省略
// 将表达式解析为getter函数,那些和组件实例对应的Watcher创建时会传递组件更新函数进来
if (typeof expOrFn === 'function') {
this.getter = expOrFn
} else {
this.getter = parsePath(expOrFn)
if (!this.getter) {
this.getter = noop
}
}
// 若非延迟watcher,立即调用getter
this.value = this.lazy? undefined: this.get()
}
// 模拟getter, 重新收集依赖re-collect dependencies.
get () {
pushTarget(this) // 往Dep.target里面添加自己
let value
const vm = this.vm
try {
// 从组件中获取到value同时触发依赖收集
value = this.getter.call(vm, vm)
} catch (e) {
} finally {
// deep watching,递归触发深层属性
if (this.deep) {
traverse(value)
}
popTarget() // 清除Dep.target
this.cleanupDeps() // 清空dep
}
return value
}
// watcher和dep相互保存引用
addDep (dep: Dep) {
const id = dep.id
if (!this.newDepIds.has(id)) {
// watcher保存dep引用
this.newDepIds.add(id)
this.newDeps.push(dep)
// 往dep里添加watcher
if (!this.depIds.has(id)) {
dep.addSub(this)
}
}
}
// 更新逻辑
update () {
if (this.lazy) {
this.dirty = true
} else if (this.sync) {
this.run()
} else {
queueWatcher(this)
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
什么时候会创建新watcher?
- 有新的组件生成的时候,1个组件=1个watcher,这时称为渲染watcher(
render watcher) - 使用了$watch或者watch方法时,这时称为用户watcher(
user watcher) - 创建计算属性的时候,这时称为计算watcher(
computed watcher)
# 数组响应化
数组数据变化采取的策略是拦截push、pop、splice等方法执行dep通知。
为数组原型中的7个可以改变内容的方法定义拦截器,\src\core\observer\array.js
// 数组原型
const arrayProto = Array.prototype
// 修改后的原型
export const arrayMethods = Object.create(arrayProto)
// 需要重写的7个方法
const methodsToPatch = [
'push',
'pop',
'shift',
'unshift',
'splice',
'sort',
'reverse'
]
// 拦截这些方法,额外发送变更通知
methodsToPatch.forEach(function (method) {
// 原始数组方法
const original = arrayProto[method]
// 修改这些方法的descriptor
def(arrayMethods, method, function mutator (...args) {
// 得到原始操作的结果
const result = original.apply(this, args)
// 获取ob实例用于发送通知
const ob = this.__ob__
// 三个能新增元素的方法特殊处理
let inserted
switch (method) {
case 'push':
case 'unshift':
inserted = args
break
case 'splice':
inserted = args.slice(2)
break
}
// 若有新增则做响应处理
if (inserted) ob.observeArray(inserted)
// 通知更新
ob.dep.notify()
return result
})
})
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
Observer中覆盖数组原型
if (Array.isArray(value)) {
// 替换数组原型
protoAugment(value, arrayMethods) // value.__proto__ = arrayMethods
this.observeArray(value)
}
2
3
4
5
defineReactive中数组的特殊处理:
// getter处理中
if (Array.isArray(value)) {
dependArray(value)
}
// 数组中所有项添加依赖,将来数组里面就可以通过__ob__.dep发送通知
function dependArray (value: Array<any>) {
for (let e, i = 0, l = value.length; i < l; i++) {
e = value[i]
e && e.__ob__ && e.__ob__.dep.depend()
if (Array.isArray(e)) {
dependArray(e)
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
# 三、Vue批量异步更新队列
Vue 在更新 DOM 时是异步执行的。只要侦听到数据变化,Vue 将开启一个队列,并缓冲在同一事件循环中发生的所有数据变更。如果同一个 watcher 被多次触发,只会被推入到队列中一次。这种在缓冲时去除重复数据对于避免不必要的计算和 DOM 操作是非常重要的。然后,在下一个的事件循环“tick”中,Vue 刷新队列并执行实际 (已去重的) 工作。Vue 在内部对异步队列尝试使用原生的 Promise.then、MutationObserver 和 setImmediate ,如果执行环境不支持,则会采用 setTimeout(fn, 0) 代替。
# queueWatcher
执行watcher入队操作,若存在重复id则跳过,\src\core\observer\scheduler.js,核心代码如下:
// 将一个观察者对象push进观察者队列,在队列中已经存在相同的id则该观察者对象将被跳过,
// 除非它是在队列被刷新时推送
export function queueWatcher (watcher: Watcher) {
const id = watcher.id // 获取watcher的id
// 检验id是否存在,已经存在则直接跳过,不存在则标记哈希表has,用于下次检验
if (has[id] == null) { // id不存在才会入队
has[id] = true
if (!flushing) {
queue.push(watcher)
} else {
// 若已刷新, 按id顺序插入到队列
let i = queue.length - 1
while (i > index && queue[i].id > watcher.id) {
i--
}
queue.splice(i + 1, 0, watcher)
}
// 若已经过了, 则下次刷新立即执行
if (!waiting) {
waiting = true
nextTick(flushSchedulerQueue) // 刷新队列并且执行watcher
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
# nextTick(flushSchedulerQueue)
vue.js提供了一个nextTick函数,其实也就是上面调用的nextTick。nextTick的实现比较简单,执行的目的是在microtask或者task中推入一个function,在当前栈执行完毕(也许还会有一些排在前面的需要执行的任务)以后执行nextTick传入的function。
nextTick按照特定异步策略执行队列刷新操作,src\core\util\next-tick.js,
# nextTick的定义
export function nextTick (cb?: Function, ctx?: Object) {
let _resolve
// 注意cb不是立刻执行,而是加入到回调数组,等待调用
callbacks.push(() => {
if (cb) {
try {
cb.call(ctx)
} catch (e) {
handleError(e, ctx, 'nextTick')
}
} else if (_resolve) {
_resolve(ctx)
}
})
// 没有处在挂起状态则开始异步执行过程
if (!pending) {
pending = true
timerFunc() // 执行timerFunc
}
// $flow-disable-line
if (!cb && typeof Promise !== 'undefined') {
return new Promise(resolve => {
_resolve = resolve
})
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
# timerFunc的定义
timerFunc 对异步队列尝试使用原生的 Promise.then、MutationObserver 和 setImmediate ,如果执行环境不支持,则会采用 setTimeout(fn, 0) 代替。
let timerFunc
// nextTick异步行为利用微任务队列,微任务比如原生的Promise.then或者MutationObserver
// MutationObserver有更广泛的支持,但是它有严重的bug,在UIWebView in iOS >= 9.3.3,
// 当触摸事件触发时会触发这个bug,即触发几次后完全停止工作。所以,我们优先使用Promise.then。
if (typeof Promise !== 'undefined' && isNative(Promise)) {
const p = Promise.resolve()
timerFunc = () => {
p.then(flushCallbacks)
//在某些有问题的uiwebview中,Promise.then没有办法正常工作,它的回调虽然可以添加到队
//列里面,但是队列不会刷新,直到浏览器需要做一些其他的工作,例如拿一个定时器。因此,我们可以
//通过添加一个空计时器来强制刷新微任务队列。
if (isIOS) setTimeout(noop)
}
isUsingMicroTask = true
} else if (!isIE && typeof MutationObserver !== 'undefined' && (
isNative(MutationObserver) ||
// PhantomJS and iOS 7.x
MutationObserver.toString() === '[object MutationObserverConstructor]'
)) {
// 不能用Promise时:PhantomJS, iOS7, Android 4.4,则使用MutationObserver
let counter = 1
const observer = new MutationObserver(flushCallbacks)
const textNode = document.createTextNode(String(counter))
observer.observe(textNode, {
characterData: true
})
timerFunc = () => {
counter = (counter + 1) % 2
textNode.data = String(counter)
}
isUsingMicroTask = true
} else if (typeof setImmediate !== 'undefined' && isNative(setImmediate)) {
// 回退到setImmediate.它利用的是宏任务队列
timerFunc = () => {
setImmediate(flushCallbacks)
}
} else {
// 最后选择setTimeout.
timerFunc = () => {
setTimeout(flushCallbacks, 0)
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
MutationObserver新建一个textNode的DOM对象,用MutationObserver绑定该DOM并指定回调函数,在DOM变化的时候则会触发回调,该回调会进入microtask,即textNode.data = String(counter)时便会加入该回调。MutationObserver使用
# 为什么要优先使用微任务?
根据 HTML Standard,在每个 macrotask(宏任务) 运行完以后,UI 都会重渲染,那么在 microtask(微任务) 中就完成数据更新,当前 macrotask 结束就可以得到最新的 UI 了。反之如果新建一个 macrotask 来做数据更新,那么渲染就会进行两次。
# 为什么要异步更新视图?
来看一下下面这一段代码
<template>
<div>
<div>{{test}}</div>
</div>
</template>
2
3
4
5
6
export default {
data () {
return {
test: 0
};
},
mounted () {
for(let i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
this.test++;
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
现在有这样的一种情况,mounted的时候test的值会被++循环执行1000次。每次++时,都会根据响应式触发setter->Dep->Watcher->update->patch。如果这时候没有异步更新视图,那么每次++都会直接操作DOM更新视图,这是非常消耗性能的。
所以Vue.js实现了一个queue队列,在下一个tick的时候会统一执行queue中Watcher的run。同时,拥有相同id的Watcher不会被重复加入到该queue中去,所以不会执行1000次Watcher的run。最终更新视图只会直接将test对应的DOM的0变成1000。保证更新视图操作DOM的动作是在当前栈执行完以后下一个tick的时候调用,大大优化了性能。
# 如何访问DOM节点更新后的数据
使用Vue.js的global API的$nextTick方法,即可在回调中获取已经更新好的DOM实例了。
<template>
<div>
<div ref="test">{{test}}</div>
<button @click="handleClick">tet</button>
</div>
</template>
2
3
4
5
6
7
export default {
data () {
return {
test: 'begin'
};
},
methods () {
handleClick () {
this.test = 'end';
this.$nextTick(() => {
console.log(this.$refs.test.innerText);//打印"end"
});
console.log(this.$refs.test.innerText);//打印“begin”
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
← 实现简易版Vue Vue源码解读(二) →
