# Koa
Koa 是一个新的 web 框架, 致力于成为 web 应用和 API 开发领域中的一个更小、更富有表现力、更健壮的基石。
koa2与koa1的最大区别是koa2实现异步是通过async/awaite,koa1实现异步是通过generator/yield,而express实现异步是通过回调函数的方式。
koa2与express 提供的API大致相同,express是大而全,内置了大多数的中间件,更让人省心,koa2不绑定任何的框架,干净简洁,小而精,更容易实现定制化,扩展性好。express是没有提供ctx来提供上下流服务,需要更多的手动处理,express本身是不支持洋葱模型的数据流入流出能力的,需要引入其他的插件。
# 一、Koa快速开始
# 开发环境
Koa 依赖 node v7.6.0 或 ES2015及更高版本和 async 方法支持。如果你的版本号小于v7.6.0,请自行升级。在确认好环境后,我们就可以新建一个项目,在里面自由操练了
$ mkdir KoaTutorial && cd KoaTutorial
$ npm i koa --save
2
# hello world 应用
const Koa = require('koa');
const app = new Koa();
app.use(async ctx => {
ctx.body = 'Hello World';
});
app.listen(3000);
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
打开浏览器,访问 http://localhost:3000/,你会看到那可爱的Hello World。就是这么简单的几行代码,我们就起了一个HTTP服务。
来看看这个hello world程序,其中前两行和后一行是架设一个 HTTP 服务。中间的则是对用户访问的处理。ctx则是Koa所提供的Context对象(上下文),ctx.body 则是ctx.response.body的alias(别名),这是响应体设置的API。
# Context 对象
Koa Context 将 node 的 request 和 response 对象封装到单个对象中,为编写 Web 应用程序和 API 提供了许多有用的方法。上例的ctx.body = ''即是发送给用户内容,它是ctx.response.body的简写。ctx.response代表 HTTP Response。ctx.request代表 HTTP Request。
# 二、Koa路由
# 使用koa-router
使用koa-router中间件,下载并引入koa-router,npm i koa-router --save
const Koa = require('koa');
const Router = require('koa-router');
const app = new Koa();
const router = new Router();
router.get('/', async (ctx) => {
let html = `
<ul>
<li><a href="/hello">helloworld</a></li>
<li><a href="/about">about</a></li>
</ul>
`
ctx.body = html
}).get('/hello', async (ctx) => {
ctx.body = 'helloworld'
}).get('/about', async (ctx) => {
ctx.body = 'about'
})
app.use(router.routes(), router.allowedMethods())
app.listen(3000);
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
# 实现简易版koa-router
实现如下:
class Router {
constructor() {
this.stack = [];
}
register(path, methods, middleware) {
let route = {path, methods, middleware}
this.stack.push(route);
}
// 现在只支持get和post,其他的同理
get(path,middleware){
this.register(path, 'get', middleware);
}
post(path,middleware){
this.register(path, 'post', middleware);
}
routes() {
let stock = this.stack;
return async function(ctx, next) {
let currentPath = ctx.url;
let route;
for (let i = 0; i < stock.length; i++) {
let item = stock[i];
if (currentPath === item.path && item.methods.indexOf(ctx.method) >= 0) {
// 判断path和method
route = item.middleware;
break;
}
}
if (typeof route === 'function') {
route(ctx, next);
return;
}
await next();
};
}
}
module.exports = Router;
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
# 三、Koa中间件
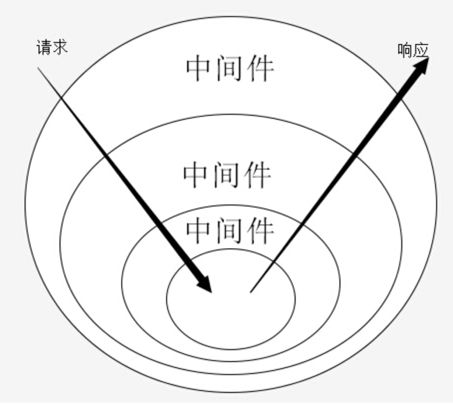
Koa 的最大特色,也是最重要的一个设计,就是中间件。Koa 应用程序是一个包含一组中间件函数的对象,它是按照类似堆栈的方式组织和执行的。Koa中使用app.use()用来加载中间件,基本上Koa 所有的功能都是通过中间件实现的。每个中间件默认接受两个参数,第一个参数是 Context 对象,第二个参数是next函数。只要调用next函数,就可以把执行权转交给下一个中间件。
下图为经典的Koa洋葱模型
我们来运行Koa官网这个小例子:
const Koa = require('koa');
const app = new Koa();
// x-response-time
app.use(async (ctx, next) => {
const start = Date.now();
await next();
const ms = Date.now() - start;
ctx.set('X-Response-Time', `${ms}ms`);
});
// logger
app.use(async (ctx, next) => {
const start = Date.now();
await next();
const ms = Date.now() - start;
console.log(`${ctx.method} ${ctx.url} - ${ms}`);
});
// response
app.use(async ctx => {
ctx.body = 'Hello World';
});
app.listen(3000);
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
上面的执行顺序就是:请求 ==> x-response-time中间件 ==> logger中间件 ==> 响应中间件 ==> logger中间件 ==> response-time中间件 ==> 响应。 通过这个顺序我们可以发现这是个栈结构以"先进后出"(first-in-last-out)的顺序执行。
# 中间件机制原理
Koa中间件机制:Koa中间件机制就是函数组合的概念,将一组需要顺序执行的函数复合(compose)为一个函数,外层函数的参数实际是内层函数的返回值。洋葱圈模型可以形象表示这种机制,是源码中的精髓和难点。
多个函数按顺序执行,后面的函数依赖前面的函数。下面实现compose函数
- 同步版
//const compose = (fn1, fn2) => (...args) => fn2(fn1(...args))
const compose = (...[first, ...other]) => (...args) => {
let ret = first(...args) // 第一个函数单独拿出来是因为第一个函数需要接受参数,而后面的函数是需要拿到前面一个函数执行的结果
other.forEach(fn => {
ret = fn(ret)
})
return ret
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
- 异步版
function compose(middlewares){
return function(){
function dispatch(i){
let fn = middlewares[i]
if(!fn){
return Promise.resolve()
}
return Promise.resolve(
fn(function next(){
return dispatch(i + 1)
})
)
}
return dispatch(0)
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
# 四、静态资源服务器
网站一般都提供静态资源(图片、字体、样式表、脚本),我们可以自己实现一个静态资源服务器,但这没必要,koa-static模块封装了这部分功能。npm i --save koa-static。
const Koa = require('koa')
const path = require('path')
const static = require('koa-static')
const app = new Koa()
// 静态资源目录对于相对入口文件index.js的路径
const staticPath = './static'
app.use(static(
path.join(__dirname, staticPath)
))
app.use(async (ctx) => {
ctx.body = 'hello world'
})
app.listen(3000)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
# 五、请求数据的获取
前文我们主要都在处理数据的响应,这儿我们来了解下Koa获取请求数据,主要为GET和POST方式。
# GET请求参数的获取
在koa中,获取GET请求数据源头是koa中request对象中的query方法或querystring方法,query返回是格式化好的参数对象,querystring返回的是请求字符串。
- 请求对象ctx.query(或ctx.request.query),返回如 { a:1, b:2 }
- 请求字符串 ctx.querystring(或ctx.request.querystring),返回如 a=1&b=2
const Koa = require('koa')
const app = new Koa()
app.use( async ( ctx ) => {
const url = ctx.url
const query = ctx.query
const querystring = ctx.querystring
ctx.body = {
url,
query,
querystring
}
})
app.listen(3000)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
运行程序并访问http://localhost:3000/?page=2&limit=10,我们将得到如下结果。
{"url":"/?page=2&limit=10","query":{"page":"2","limit":"10"},"querystring":"page=2&limit=10"}
# POST请求数据获取
对于POST请求的处理,koa2没有封装获取参数的方法,需要通过自己解析上下文context中的原生node.js请求对象req,将POST表单数据解析成querystring(例如:a=1&b=2&c=3),再将querystring 解析成JSON格式(例如:{"a":"1", "b":"2", "c":"3"}),我们来直接使用koa-bodyparser 模块从 POST 请求的数据体里面提取键值对。
const Koa = require('koa')
const app = new Koa()
const bodyParser = require('koa-bodyparser')
// 使用koa-bodyparser中间件
app.use(bodyParser())
app.use(async (ctx) => {
if (ctx.url === '/' && ctx.method === 'GET') {
// 当GET请求时候返回表单页面
let html = `
<h1>koa-bodyparser</h1>
<form method="POST" action="/">
Name:<input name="name" /><br/>
Age:<input name="age" /><br/>
Email: <input name="email" /><br/>
<button type="submit">submit</button>
</form>
`
ctx.body = html
} else if (ctx.url === '/' && ctx.method === 'POST') {
// 当POST请求的时候,中间件koa-bodyparser解析POST表单里的数据,并显示出来
ctx.body = ctx.request.body
} else {
// 404
ctx.body = '<h1>404 Not Found</h1>'
}
})
app.listen(3000)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
运行程序,填写并提交表单,请求结果为:
{
name: "ogilhinn",
age: "120",
email: "ogilhinn@gmail.com"
}
2
3
4
5
